Careers
At Snowdon Village Academy, careers education, information, advice and guidance is at our forefront ensuring all our students leave with the right tools and values to help prepare them for adulthood. We support students to consider their future options, realise their potential and decide how their skills and experiences fit with opportunities in the job market. We prepare students for their preferred transitional pathway whether that is to continue with further education, employment, training or living independently and we use a person-centred approach in our delivery method.
We are fully committed to our statutory and moral obligation to provide a holistic careers service to students within our Academy as part of our 3-19 Curriculum Programme, highlighting the vocational and academic routes to their preferred careers path.
It is important that all students are fully supported and guided through the process of planning their futures. With a Team of Career Co-Ordinators led by a Careers Lead leading on a programme of education, information, advice and guidance for all students from Years 3 -19 we believe our students should be well prepared for their futures. All staff at Snowdon Village Academy play an active role in preparing them.
We believe the programme enables all our learners to develop self-agency in their learning journey and becomes confident and autonomous learners who are able to make positive and engaging career choices with the opportunities available to them. We ensure that students are inspired and motivated for the world of world, ensuring high achievable aspirations are considered for a range of careers available. Our Careers Strategy works in line with our PSHE policy.
We work closely with the local authority and multi-agency groups due to the vulnerable nature of our students who all have special education needs and disabilities with Education, Health and Care plans in place, ensuring that we know of all the services available to support students, to access these and share this knowledge amongst our community. We all share the presumption that for many of our young people with special educational needs and disabilities are capable of sustaining paid employment with the right preparation and support. We regularly celebrate and showcase and promote the achievements of our students who are volunteering or in paid employment at every possible opportunity.
We underpin our strategy with the Gatsby Benchmark and our specialism of Applied Learning.
We therefore have a full programme of careers education that is delivered through the Life Skills Curriculum, PHSE, Special Events (Showcase), Enrichment Programmes, visits, trips and assemblies and also within subject areas and tutor time across the Academy.
Expectations for Students:
All students will:
- Develop a deeper understanding of themselves, their abilities and affinities
- Gain a greater knowledge of the range of opportunities open to them
- Take part in work related activities in and out of school
- Understand the labour market and the requirements and expectations of employers
- Learn to make decisions wisely about their future
- Be fully prepared to manage change and be fully supported through key transition periods
- Learn how to improve their own employability: how to find work, how to get work and how to progress their careers
Structure of the Programme
We have a Work Experience Programme that is flexible to our student’s needs and is arranged on an individual basis in line with each student’s aspirations and abilities. We utilise the services of Career Co-Ordinators to help prepare students, locate suitable placements and monitor student’s progress. We have a team of trained Academy Career Co-Ordinators who will meet with students individually to discuss aspirations, opportunities, entry requirements and help students apply for courses, jobs and apprenticeships.
All students can meet with their School Careers Co-Ordinator for individual advice sessions about options, future choices, CV clinic, interview preparation, apprenticeship applications, and any other guidance they need.
There is a clear timetabled session for 1:1 guidance appointment scheduled throughout the Academic Year together with planned Careers Events as part of the school planner. We work together with all our stakeholders including parents, guardians and community governor responsible for careers and advice to support the programme.
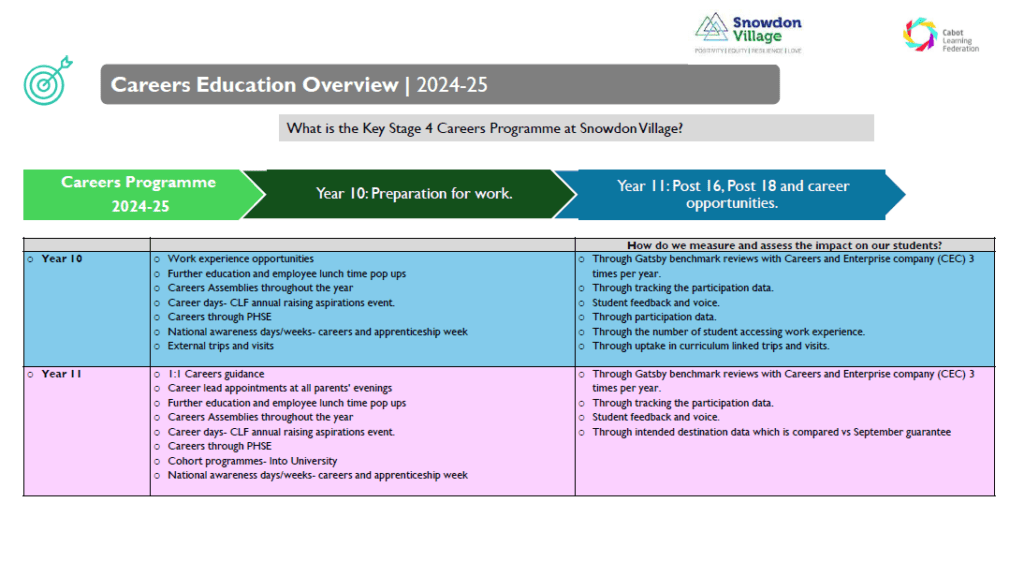
At Snowdon Village, we have broken down our Careers Programme into Key Stage Group to ensure all our students receive the appropriate support.
Key Stage 2
| Key Stage 2 | ||||||||
| Learning Objectives Learners should learn to… | Gatsby reference | Possible teaching activities | Learning outcomes Learners will be… | |||||
| Developing yourself through careers, employability and enterprise education | ||||||||
| (1) Describe what you are like, what you are good at and what you enjoy doing | 3 | You know what you like and enjoy doing You can describe what you are good at · Learners describe themselves to their e-pen pals · Learners keep learning diaries · Learners do card sorts to identify personal attributes that are ‘Like me’, ‘Not much like me’ | Self-aware | |||||
| (2) Explain how to get what you want | 3 | You can speak positively about yourself and what you have done so far to make things happen · Learners draw or write the things they would use or wear in a job they would like to do and talk to someone about it · Learners imagine that they have three wishes · Learners talk positively about what they would like to do | Self-determined | |||||
| (3) Identify what you like about learning from careers, employability and enterprise activities and experiences | 3 | You can describe what you have learnt and enjoyed from career, employability and enterprise learning activities and experiences · In circle time, Learners talk about what is different about learning from a visitor rather than a teacher · The class give an assembly on what they gained from visiting a local university/college/secondary school | Self-improving as a learner | |||||
| Learning about careers and the world of work | ||||||||
| (4) Give examples of what it means to have a career | 2 | Using famous people e.g. authors, sports people look at how their careers developed
· ‘Who am I?’ quiz. Teacher reveals ten clues, one at a time, about the career of someone known to Learners who have to guess who the person is. The teacher uses this as an opportunity to discuss different career patterns and structures · Learners describe the career of someone they admire either in the style of a story or in the style of a journey. Afterwards, they compare the different treatments | Exploring careers and career development | |||||
| (5) Give examples of what people like and dislike about the work they do | 2 | From interviewing family and visiting speakers you can identify different kinds of work that people do.
· Learners interview visitors about what they like most and what they like least about their jobs · Learners distinguish between ‘paid work’ and ‘gift work’, then ask a few selected people how they feel about both kinds of work that they do | Investigating work and working life | |||||
| (6) Describe a local business, how it is run and the products and/or services it provides | 5 | You are aware of the different local businesses and the products and services offered
· Do a project on shops and businesses in the high street · As part of a healthy eating project, a local chef and restaurant owner comes into school to do a talk and demonstration, then judge a competition where Learners plan their own menus | Understanding business and industry | |||||
| (7) Describe the main types of employment in your area: past, present and emerging | 5 | As part of your local history project you can state what have been the changes in employment in your village/town
· Learners use ‘then’ and ‘now’ photos of local workplaces to discuss the changing world of work where they live · Learners attempt a simple classification of present-day occupations that they can find within 200 metres of the school | Investigating jobs and labour market information (LMI) | |||||
| (8) Recognise the harm caused by stereotyping and discrimination and the importance of treating people fairly | 3 | You can say how people should be treated and know who to talk to if something is wrong · Learners write their own accounts of news stories about discrimination and exploitation at work · Learners find out about the work and values of a charity that tackles social deprivation · Learners run a campaign to promote awareness of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child | Valuing equality, diversity and inclusion | |||||
| (9) Be aware of how to keep yourself safe and well when you are learning and playing | 4 | You can follow safety rules to keep yourself and others safe when working at school.
· Learners find out the local by-laws on working hours and restricted occupations relating to children and young people · Learners run a ‘safety in the classroom’ campaign | Learning about safe working practices and environments | |||||
| Developing your career management and employability skills | ||||||||
| (10) Be aware of where to get impartial information and support when you need it and how to make good use of it | 2 | You can identify when you may need help or assistance and who can provide it whilst at school
· Older students tell younger students in a class blog about life in secondary school/16+ · Learners take part in a ‘people who help us’ class project | Making the most of careers information, advice and guidance (CEIAG) | |||||
| (11) Identify key qualities and skills that employers are looking for | 4,5,6 | You can identify the skills and qualities needed for this job using personal experiences
· Learners play a careers discussion game using work problem cards, e.g. ‘What would happen if a bus driver turned up late for work?’ · Learners write a job description for a babysitter and hold mock interviews | Preparing for employability | |||||
| (12) Show that you can use your initiative and be enterprising | 4,5,6 | You can show how to work in a team and bring your talents to complete a challenge
· Learners run a charity fund-raising event, e.g. a pet show or a plant stall · Learners take part in a design, production and marketing game, e.g. making and selling varieties of crackers for different occasions | Showing initiative and enterprise | |||||
| (13) Show that you can make considered decisions about saving, spending and giving | 3 | You can show how to make an informed decision based on looking at a range of saving products
· Learners keep a pocket book with details of all their income and outgoings · Learners compare terms and conditions on a range of Learners’ savings products | Developing personal financial capability | |||||
| (14) Be able to compare information about the secondary education choices open to you | 2 | You can identify who are the next providers of education in your area
· Learners make a ‘To do’ list of things they want to find out and tick them off after they’ve done them · Learners make a podcast of their impressions of secondary school after attending a ‘taster day’ | Identifying choices and opportunities | |||||
| (15) Know how to make plans and decisions carefully | 3 | You can say what you will need to do differently when taking on a new challenge
· Learners make a T-chart and list the pros and cons of a choice they are considering · Learners have a discussion using two piles of cards: one pile with examples of decisions that they might be faced with and another pile with examples of different styles of making decisions. They turn up one card from each pile and discuss the consequences of making that particular decision in that way | Planning and deciding | |||||
| (16) Know how to make a good impression on other people | 3 | You can say what you need to do to impress people in a given situation
· Learners interview other Learners for positions on the School Council · Learners write a personal manifesto for a mock election | Handling applications and interviews | |||||
| (17) Identify ways of making successful transitions such as the move from primary to secondary school | 7 | You can set yourself realistic goals in making the next transition
· In circle time, Learners discuss their feelings as they prepare to leave their present school and move to a new one · Learners use ‘Google maps – street view’ to trace their journey from home to their new school | Managing changes and transitions | |||||
Key Stage 2 Learning Outcomes
- Identifying personal strengths and weaknesses
- Sharing your strengths with your peers and giving examples of how you have achieved things e.g. a music award, gymnastics certificate, math’s challenge
- Inviting a visitor in to talk about themselves and being able to ask questions about their career pathway
- Using famous people identify the career path they have followed from age 16; identify their achievements, challenges
- List the types of work; seasonal, part-time, full time, self-employed, portfolio, being a parent
- Look at businesses in a five-mile radius and place as either a ‘product’ or a ‘service’
- Identifying and understanding the changes to employment that have taken place in your local area
- Understand the purpose and benefits for having rights and the responsibilities that come with them
- Health and safety around the school, risk and hazard assessments in practical situations
- Friendship groups and buddies, personal safety and social media, networking
- Communication, motivation, shows empathy, problem solving,
- Creative, innovative, team working, enjoys a challenge
- Pocket money or savings, My Money Week
- Exploring the options, looking at school/academy websites, attending open/induction days
- Use of the Make It Real Game, citizenship type scenarios
- Personal statement, personal presentation tips
- Set personal goals, read the next school’s information from the open day/prospectus
Key Stage 3
| Key Stage 3 | |||
| Learning Objectives Learners should learn to… | Gatsby reference | Possible teaching activities | Learning outcomes Learners will be… |
| Developing yourself through careers, employability and enterprise education | |||
| (1) Describe yourself, your strengths and preferences | 3 | You can talk about your strengths You know what you like and enjoy doing
• Learners participate in a Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning (SEAL) programme to develop their self and social awareness, manage their feelings and become more effective learners • Learners complete a range of self-assessment exercises and record the results in their e-portfolios | Self-aware |
| (2) Be able to focus on the positive aspects of your wellbeing, progress and achievements | 3 | You can tell your own story, how you are making progress and what you need to do to raise your achievement and improve your wellbeing
• Learners tell the story of their earliest memories of what they were good at and interested in. They look at their story for clues about what they are like today • As in medieval times, Learners use pictures and symbols on a personal shield to identify who they are and tell others about themselves | Self-determined |
| (3) Explain how you are benefitting as a learner from careers, employability and enterprise activities and experiences | 3 | You can explain what you have learnt from career, employability and enterprise learning activities and experiences
• In their small group, Learners review their experience of taking responsibility for interviewing a visitor • Learners keep a skills log | Self-improving as a learner |
| Learning about careers and the world of work | |||
| (4) Describe different explanations of what careers are and how they can be developed | 2 | Using the members of staff around you survey how their careers developed. You can spot similarities and differences
• Learners find out how the careers of different members of staff have developed and then reflect on the similarities and difference between them • Learners create career timelines to summarise the career of someone they admire | Exploring careers and career development |
| (5) Give examples of different kinds of work and why people’s satisfaction with their working lives can change | 2 | You can identify different kinds of work that people do. You can say why people’s job satisfaction varies
• In small groups, Learners research a job family and give ‘table presentations’ at their own careers fair • Learners find out the purpose of work clothes/uniforms and whether people like or dislike wearing them (linked to a school non-uniform day) • Learners read and discuss poems about work and working life | Investigating work and working life |
| 6) Give examples of different business organisational structure | 5 | Looking at different businesses you can describe their organisation and structure
• Learners investigate the types of businesses involved in the exploitation of commodities such as coffee from the raw material stage to the finished product • Learners list the jobs involved in getting an everyday item such as a tin of beans to consumers • Learners make a spider diagram of the contractors and suppliers linked to their own school | Understanding business and industry |
| (7) Be aware of what labour market information (LMI) is and how it can be useful to you | 5 | You can say what is LMI and why you need to be aware of it for making future decisions
• Learners investigate opportunities for women in the STEM (science, technology, engineering and math’s) industries • Learners analyse local job vacancies using job vacancy websites/apps and newspapers • Learners investigate the features of jobs in the ‘primary’ labour market (e.g. high wages and benefits, longer lasting careers) and compare them with jobs in the secondary labour market (e.g. low wage, limited mobility within jobs and temporary careers) | Investigating jobs and labour market information (LMI) |
| (8) Identify how to stand up to stereotyping and discrimination that is damaging to you and those around you | 3 | You can say how to stand up to stereotyping and discrimination that is damaging to you and those around you • Learners ask their alumni mentors for advice on how to combat stereotyping and discrimination • Learners plan a programme of activities for Black History or LGBT Month focusing on landmark workplace discrimination cases | Valuing equality, diversity and inclusion |
| (9) Be aware of the laws and bye-laws relating to young people’s permitted hours and types of employment; and know how to minimise health and safety risks to you and those around you | 4 | You are aware of the laws and the bye-laws relating to the hours and types of employment for your age group
• Learners write a true or false quiz to test other Learners’ knowledge of the laws and by-laws relating to the employment of school-age children • Learners discuss how to avoid the problems shown in a cartoon picture of hazards in the workplace | Learning about safe working practices and environments |
| Developing your career management and employability skills | |||
| (10) Identify your personal networks of support, including how to access and make the most of impartial face-to-face and digital careers information, advice and guidance service | 2 | You can use family and friends to access advice and information and can appreciate the role of impartiality and sources of partiality. You take part in employer led activities to develop your networking skills
• Learners create a mind map or visual representation of their networks of careers influencers and supporters • Learners produce a guide to ‘making the most of information, advice and guidance’ in their school | Making the most of careers information, advice and guidance (CEIAG) |
| (11) Recognise the qualities and skills you have demonstrated both in and out of school that will help to make you employable | 4,5,6 | You can recognise the skills and qualities needed for the world of work through activities/experiences • Learners watch short video clips and identify the qualities and skills that support employability • Learners maintain a skills log recording their best demonstrations of the qualities and skills needed for employability | Preparing for employability |
| (12) Recognise when you are using qualities and skills that entrepreneurs demonstrate | 4,5,6 | You can show how you are using the qualities and skills when being enterprising as part of ‘drop-down’ days, challenges, through subjects
• Learners maintain a skills log recording their best demonstrations of the qualities and skills needed for employability • Learners gain experience of event planning by working out the programme, timings, publicity and budget for a school event such as a fashion show or pet show. They review their contribution to the venture • Learners plan and deliver a series of environmental awareness projects as part of their school’s ‘green school’ campaign | Showing initiative and enterprise |
| (13) Show that you can manage a personal budget and contribute to household and school budgets | 3 | You can show how to get the most from a personal budget, understand and use financial words
• Learners take part in a simulation that challenges them to manage a household budget • Learners use a personal budget planner to work out a budget for the summer holidays | Developing personal financial capability |
| (14) Know how to identify and systematically explore the options open to you at a decision point | 2 | You can make an informed decision after assessing the choices and opportunities open to you • Learners brainstorm the criteria they will use to compare the subjects available to them at Key Stage 4 • Learners produce subject posters giving the facts about the qualifications, skills and jobs they can gain by studying particular subjects | Identifying choices and opportunities |
| (15) Know how to make plans and decisions carefully including negotiating with those who can help you get the qualifications, skills and experience you need | 3 | You can research for the skills, qualifications and experience you need to discuss and where necessary negotiate your plans for the future
• Groups form small company teams to promote tourism in the local area. They have to negotiate their roles in the team and the main features of the campaign • Learners engage in target-setting and review activities with their tutors and subject teachers | Planning and deciding |
| (16) Know how to prepare and present yourself well when going through a selection process | 3 | You can prepare and present yourself well when going through a selection process
• Learners apply for leadership roles in the school, e.g. as School Council representatives, peer mentors • Learners role play doing well in informal or unusual interview situations, e.g. being interviewed for a part-time job in a shop when the interviewer keeps breaking off to serve customers | Handling applications and interviews |
| (17) Show that you can be positive, flexible and well- prepared at transition points in your life | 7 | You can be positive, flexible and well prepared for your move into key stage 4
• Y8/9 Learners have back-up plans in case they cannot have all their first-choice options • Learners write a guide for Year 6 Learners on how to make a success of the move from primary to secondary school | Managing changes and transitions |
Key Stage 3 Learning Outcomes
- Self-assessment, peer assessment, using an ILP (e-portfolio)
- Transition from primary/middle/secondary school, understand feelings and changes to learning styles
- Inviting a visitor in to talk about themselves, curriculum ‘drop down’ days, work shadowing
- Interview staff, using various means of communication (Zoom, Teams etc.)
- Interview staff about their career pathway.
- Look at businesses in a five-mile radius and place into categories of small, medium and large, identify the differences
- Understand the terminology of SIC and SOC, explain STEM subjects, do we need another hairdresser?
- Understand issues of protected characteristics including race, religion, gender, age, disability
- Personal safety, health and safety at work, roles and responsibilities, hours, impact on learning
- Friendship groups, personal safety and social media, networking
- Attendance, punctuality, communication, motivation and professional conduct
- Personal profile, certificates of participation/achievement, citizenship, character and resilience
- Pocket money or savings, Pfeg (now part of Young Enterprise) website, RBS money sense, account,
- Options process, parent evenings, subject assemblies, using the careers resource centre, careers fairs, contact with local employers
- Use of the Real Game, citizenship type scenarios
- Personal statement, basic CV knowledge, personal presentation tips
- Action plan, complete ILP and set personal goals
Key Stage 4
| Key Stage 4 | |||
| Learning Objectives Learners should learn to… | Gatsby reference | Possible teaching activities | Learning outcomes Learners will be… |
| Developing yourself through careers, employability and enterprise education | |||
| (1) Recognise how you are changing, what you now have to offer, what is important to you | 3 | • Learners complete an occupational interests’ questionnaire and discuss the results with their mentor • Learners describe what they like about how they have changed since Year 7 | Self-aware |
| (2) Be positive about you own story and the responsibility you are taking for your own progress, achievements and wellbeing | 3 | • Learners write a chapter of their ‘career story’ about a recent success and talk to a partner about how that episode has influenced the way they think about themselves • Learners set personal and learning targets to build on their strengths rather than eradicate their weaknesses | Self-determined |
| (3) Review and reflect upon how you have benefitted as a learner from career, employability and enterprise learning activities and experiences | 3 | • Learners choose the most important aspects of an experience they have just had and reflect on what they have learned. They repeat the activity after a period of time to see if their perspective has changed • Students who have had placements in similar working environments compare and contrast what they learnt from their work experience
| Self-improving as a learner |
| Learning about careers and the world of work | |||
| (4) Explain key ideas about your career and career development | 2 | • Learners weigh up the pros and cons of single-track careers, serial careers, portfolio careers and lifestyle careers • Learners explore the dynamics of ‘occupational’ careers (e.g. teaching), ‘organisational’ careers (e.g. in the Army) and ‘boundaryless’ careers characterised by frequent job switching | Exploring careers and career development |
| (5) Explain how work is changing and how this impact on people’s satisfaction with their working lives | 2 | • Learners analyse stories in the news about the factors that affect the mental health of workers • Learners talk to alumni about how their jobs are likely to change in the next 5-10 years | Investigating work and working life |
| (6) Explain 3 different types of businesses, how they operate and how they measure success | 5 | • Learners look at the pros and cons of different kinds of business entities, e.g. sole trader, partnership, company and franchise in the private sector • Learners compare and contrast their experience of taking part in two different enterprise simulations – one based on a share-holder model and the other based on a co-operative model | Understanding business and industry |
| (7) Find relevant job and labour market information (LMI) and know how to use it in your career planning | 5 | • Learners analyse national and local data on the destinations of last year’s leavers and consider possible implications for their own plans • Specially trained Learners show their peers how to use online LMI sources | Investigating jobs and labour market information (LMI) |
| (8) Recognise and challenge stereotyping, discrimination and other barriers to equality, diversity and inclusion. know your rights and responsibilities in relation to these issues | 3 | • Learners interview employers about good practice in carrying out their duties under the Equality Act 2010 ‘to make reasonable adjustments to their workplaces to overcome barriers experienced by disabled people’ • Learners investigate progress in tackling ‘the glass ceiling’ in the leading professions, e.g. engineering, architecture, law, medicine, accountancy | Valuing equality, diversity and inclusion |
| (9) Be aware of your responsibilities and rights as a student, trainee or employee for following safe working practices | 4 | • Learners carry out a risk assessment of an indoor space at school, e.g. a laboratory, classroom, dining hall, cloakroom • Learners research health and safety requirements and guidelines for tools and equipment that they use, e.g. VDU, keyboard, machine tools in the Design and Technology workshop
| Learning about safe working practices and environments |
| Developing your career management and employability skills | |||
| (10) Build and make the most of your personal network of support including how to identify and use a wide range of careers information, advice and guidance and distinguish between objectivity and bias | 2 | • Learners discuss their options with family, friends/social network, school staff and careers specialists and carefully weigh up the advice received • Learners examine through case studies what impartiality means when it is applied to careers guidance practice | Making the most of careers information, advice and guidance (CEIAG) |
| (11) Show how you have acquired and are developing qualities and skills to improve your employability | 4,5,6 | • Learners use the Centre for Education and Industry (CEI) Learning Frameworks to record key skills and plan and carry out work experience tasks • Learners practice filling out the sections on sample application forms that ask them to provide evidence of the skills and qualities that they have demonstrated | Preparing for employability |
| (12) Show that you can be enterprising in the way you learn, work and manage your career | 4,5,6 | • Local employers run a session on techniques of successful marketing and then set a marketing challenge such as how to promote healthy eating • Learners assess themselves on the career adaptability scale and discuss with their tutor how they are going to follow up the results | Showing initiative and enterprise |
| (13) Show that you can manage your own money Understand personal finance documents Know how to access financial support for further study and training | 3 | • Learners calculate the cost of higher education and how the return on their investment can be managed • Learners complete online modules explaining tax and national insurance matters | Developing personal financial capability |
| (14) Research your education, training, apprenticeship, employment and volunteering options including information about the best progression pathways through to specific goals | 2 | • Learners draw up a list of questions to ask stallholders that they want to meet at a forthcoming careers fair • Learners watch a theatre group production on ‘Your Choices at 16+’ and then participate in a discussion workshop about what it means to them | Identifying choices and opportunities |
| (15) Know how to make important plans and decisions Know how to solve problems Deal appropriately with influences on you | 3 | • Learners learn how to weigh up different factors affecting their decisions by using the decision matrix method • Learners take part in role plays to practice using the three main styles of communication and conflict resolution (i.e. being passive, assertive or aggressive) | Planning and deciding |
| (16) Know you rights and responsibilities in a selection process and the strategies to use to improve your chances of being chosen | 3 | • Learners take part in a mock interview for a suitable position (e.g. an apprenticeship, a college place or a job) and prepare a CV beforehand • Learners complete a ‘true’ or ‘false’ quiz about questions relating to equality of opportunity that interviewers are not allowed to ask candidates | Handling applications and interviews |
| (17) Review and reflect on previous transitions to help you improve your preparation for future moves in education, training and employment | 7 | • Learners recall the range of experiences that they and others had when making decisions at 13+ and suggest how the lessons learnt can be applied to their decisions at 16+ • Learners say what they think should be in an induction programmes for young people going into the sixth form, a college, work-based learning or an apprenticeship | Managing changes and transitions |
Key Stage 4 Learning Outcomes
- Attitude. Skills and experience. Money, value, travel time, career.
- Improved behaviour, attendance. Work experience or academic achievement.
- Skills, references, open evenings, events.
- Career websites e.g. Plotr, i-could, zoom, teams Interviews, talking to family and employers.
- Hours, mobile market. Changing careers, portfolio workers, zero-hour contracts
- Bank, builders, fashion shop. Shareholders any current value, do they pay dividends? Goodwill.
- How many bricklayers/ physios/ people working in the ‘green’ industry will be needed in 5 years’ time good website Warwick University – ‘LMI for All’
- Race, religion, age, disabilities and any other barriers to equality and inclusion
- Health and safety at work
- Talking to employers, college interviews, part time jobs
- Work experience, improved attendance, college course,
- Do you have your own portfolio? Have you been a sports captain? Library monitor.
- Pocket money or savings. PFEG materials now part of Young Enterprise website. Bank websites. Knowledge of ISA etc. The cost of an Apprenticeship against attending an HEI
- Open evenings, taster days, company websites.
- How are you making decisions and plans? are family involved? Have you had to solve any problems?
- Sample questions that interviewers can and cannot ask – Age, sex, ethnicity, Grades, references, good CV writing.
- Update CV. Improve Personal Statement. Reference, include taster day visits.